

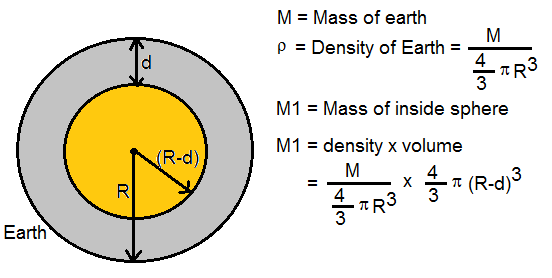
The time it takes to reach the ground (without air resistance) can be calculated by rearranging (4): Acceleration of gravity on the North and South Pole - and on EquatorĪ stone is dropped from 1470 ft (448 m) - approximately the height of Empire State Building.The air resistance - or drag force - for objects at higher velocities can be significant - depending on shape and surface area. Note! Velocities and distances are achieved without aerodynamic resistance ( vacuum conditions).
Gravity acceleration free#
The velocity and distance traveled by a free falling object:
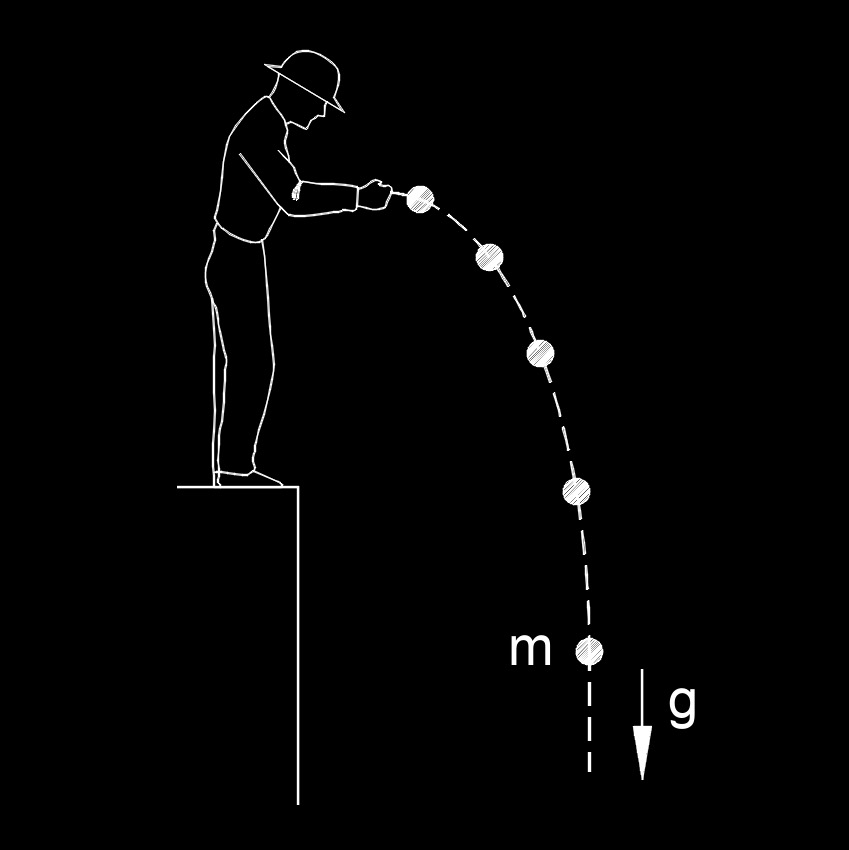
The distance traveled by a free falling object after some time can be expressed as: The velocity for a free falling object after some time can be calculated as: Velocity and Distance Traveled by a Free Falling Object a heavy and a light body near the earth will fall to the earth with the same acceleration (when neglecting the air resistance)ġ a g = 1 g = 9.81 m/s 2 = 35.30394 (km/h)/sĪcceleration of Gravity in Imperial Unitsġ a g = 1 g = 32.174 ft/s 2 = 386.1 in/s 2 = 22 mph/s.The acceleration of gravity can be observed by measuring the change of velocity related to change of time for a free falling object:Īn object dropped in free air accelerates to speed 9.81 m/s (32.174 ft/s) in one - 1 - second. force is a vector - a quantity with magnitude and direction.mass is a property - a quantity with magnitude.

The force caused by gravity - a g - is called weight. Newton's second law for the gravity force - weight - can be expressed asĪ g = g = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s 2, 32.17405 ft/s 2) "Change of motion is proportional to the force applied, and take place along the straight line the force acts." The magnitude of the effect depends on the air density (and hence air pressure) or the water density respectively see Apparent weight for details.Acceleration of Gravity is one of the most used physical constants - known from Newton's Second Law In air or water, objects experience a supporting buoyancy force which reduces the apparent strength of gravity (as measured by an object's weight). There is a strong correlation between the gravity derivation map of earth from NASA GRACE with positions of recent volcanic activity, ridge spreading and volcanos: these regions have a stronger gravitation than theoretical predictions. The areas where NASA GRACE measured gravity to be stronger than the theoretical gravity have a strong correlation with the positions of the volcanic activity and ridge spreading. The actual depth dependence of density and gravity, inferred from seismic travel times (see Adams–Williamson equation), is shown in the graphs below.Ī map of recent volcanic activity and ridge spreading. It is a vector (physics) quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the norm g = ‖ g ‖ The gravity of Earth, denoted by g, is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). Red shows the areas where gravity is stronger than the smooth, standard value, and blue reveals areas where gravity is weaker. Earth's gravity measured by NASA GRACE mission, showing deviations from the theoretical gravity of an idealized, smooth Earth, the so-called Earth ellipsoid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
